Introduction
The compacting test is one methods used to determine the workability of fresh concrete (other methods include Slump Test and Vee-bee Consistometer Test). The workability of concrete is a property which describes the ease of working on the concrete. In other words, it is a measure of how easily fresh concrete can be placed and compacted. This test is believed to produce more accurate results compared to slump test. However, like slump test, accuracy in the results reduces with increase in aggregate sizes.
This test simply measures the weight of a partially compacted concrete and compares this to the fully compacted weight of the same sample. The ratio of the former to the latter is known as the Compaction Factor.
Objective(s) of the Experiment
The test is carried out to determine the workability of concrete, using the compaction factor method.
Equipment Needed
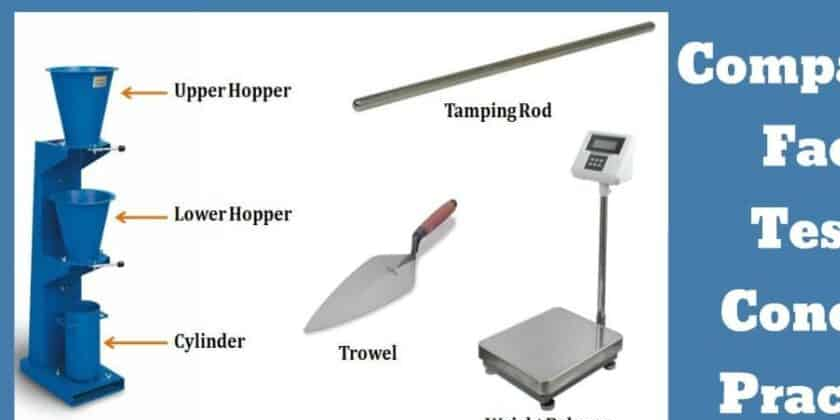
- The Compaction Factor Apparatus: this consists of two conical hoppers mounted above a cylinder as shown below.
- Compacting Rod
- Hand Float
- Hand Trowel
- Scoop
- Weighing Balance

Procedures
- Clean and dry the compaction factor apparatus; and weigh the cylinder. Record this weight as “Weight of Cylinder (Wc)”.
- Using the scoop, fill the concrete into the upper hopper and level the concrete excess
- Open (release) the trap door of the hopper such that the concrete freely falls into the lower hopper. Concrete sticking to the sides of the mould should be pushed downwards with a steel rod.
- The trap door of the lower hopper is then opened and the concrete allowed to fall into the cylinder.
- With two slid float across the top of the mould, cut off excess concrete.
- Wipe and clean the outer part of the cylinder and weigh to the nearest 10g. Record this weight as “Weight of Cylinder + Weight of Partially Compacted Concrete (Wcp)”.
- Empty the cylinder and refill it with concrete from the same sample. The filling is done in three layers and each layer is compacted with the compacting rod 25 times.
- Level the surface of the cylinder and clean the outer part.
- Weigh the cylinder with the compacted concrete also to the nearest 10g. Record this weight as “Weight of Cylinder + Weight of Fully Compacted Concrete (Wcf)”.
Results and Calculations
- Weight of Cylinder, Wc = ________
- Weight of Cylinder + Weight of Partially Compacted Concrete (Wcp) =_______
- Weight of Cylinder + Weight of Fully Compacted Concrete (Wcf) = ________
- Weight of Partially Compacted Concrete (Wp) = Wcp – Wc = _________
- Weight of Fully Compacted Concrete (Wf) = Wcf – Wc = ________
- Compaction Factor = Wp / Wf
- The compaction factor is reported in 2 decimal places.
Discussion and Conclusion
- Compaction factor normally falls between the range of 0.8 – 0.92
- This test gives more accurate results than slump test while dealing with relatively dryer concrete mixes.
- Compaction factor test gives more precise and sensitive results.
- Compaction factor of 0.75 to 0.80 are used for concreting of shallow sections with vibrations; 0.80 – 0.85 for concreting lightly reinforced sections with vibrations; 0.85 – 0.92 for concreting of lightly reinforced sections without vibrations or heavily reinforced sections with vibrations; and compaction factors above 0.92 are used for concreting heavily reinforced sections without vibrations. The mixture consistency of concrete can be defined by referring to the table below:

References
- Atom, M.T. (2002). “Compaction Factor Test”. Civil Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering and Technology, University of Jordan.
- CivilBlog. “Different Test Methods for Workability Measurement”. http://civilblog.org/category/concrete-technology/
- Haidar, B. (2015). “Compaction Factor Test”. Laboratory Instruction Manual for CE216: Building Materials & Concrete Technology, Civil Engineering Department, Ishik University.