Introduction
The Los Angeles (LA) abrasion test is a common test method used to evaluate the hardness of coarse aggregates such as gravel, crushed rock, and recycled concrete. The test is used to measure the abrasion resistance of the aggregate and is often used in the construction industry to determine the suitability of aggregates for use in various applications such as road construction and concrete production.
Why is the LA Abrasion Test Important?
The LA abrasion test is an important test because it helps to determine the quality of the aggregate being used. The test measures the ability of the aggregate to resist abrasion and wear and tear, which is important for ensuring the longevity and durability of the finished product. For example, if an aggregate has a high LA abrasion value, it is likely to wear down quickly when used in road construction, which can lead to costly repairs and maintenance in the future.
Objective(s) of the Experiment
The objective of the LA abrasion test is to determine the abrasion resistance of coarse aggregates.
Equipment and Materials Needed
- Los Angeles abrasion testing machine
- Oven
- Sieve with a 1.70 mm opening
- Balance with a capacity of 10 kg and accuracy of 0.1 g
- Round steel balls
- Tray
Procedure
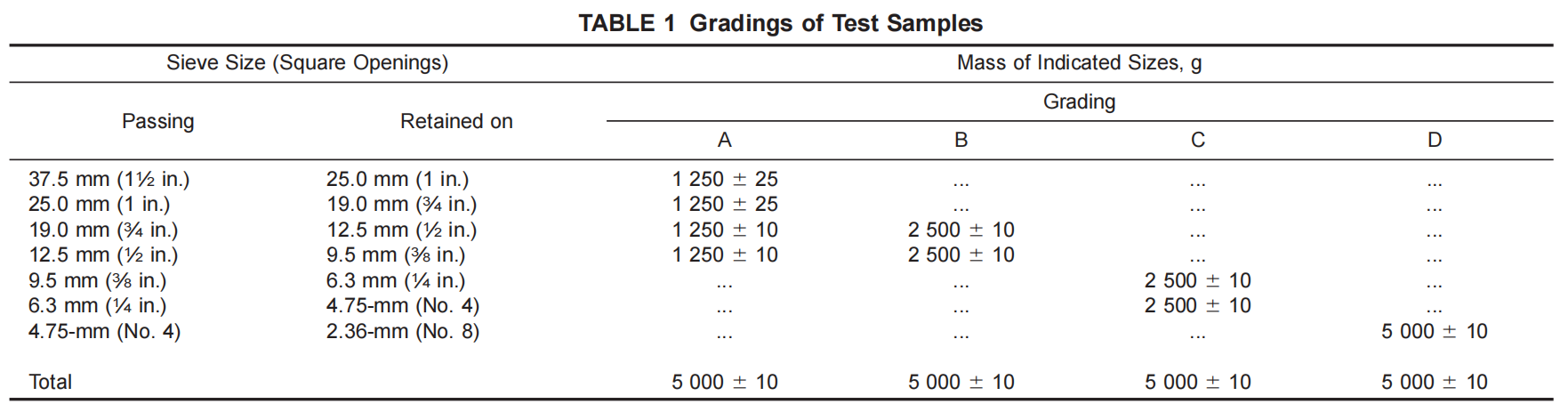
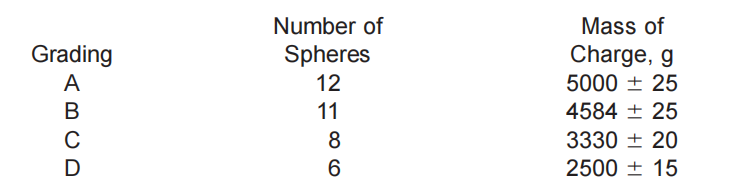
- Prepare the test sample by drying the coarse aggregate in an oven at a temperature of 105°C to 110°C until it reaches a constant weight. The sample should be approximately 5000 g, selected in accordance with Table 1 above.
- Pour the aggregate into the Los Angeles abrasion testing machine and add a specified number of round steel balls. The number of steel balls used depends on the size of the machine and the aggregate being tested. Typically, 12 steel balls are used for aggregates larger than 38 mm, and 8 steel balls are used for aggregates smaller than 38 mm (Use Table 2 above).
- Run the machine for a specified number of revolutions, depending on the hardness of the aggregate being tested. The machine rotates the steel balls and the aggregate in a drum, causing the aggregate to be subjected to abrasion and impact. A typical test duration is 100 revolutions for aggregates larger than 38 mm and 500 revolutions for aggregates smaller than 38 mm.
- After the specified number of revolutions, remove the aggregate from the machine and separate it using the sieve with a 1.70 mm opening. The material that passes through the sieve is weighed and recorded as the Los Angeles abrasion loss.
Results and Calculations
The Los Angeles abrasion loss is calculated as the difference between the original weight of the test sample and the weight of the material that passed through the sieve, divided by the original weight of the test sample, expressed as a percentage. The result is reported as the LA abrasion value.
LA abrasion value = (Original weight – Weight passing 1.70 mm sieve) / Original weight x 100%
Notes:
- The LA abrasion test should be performed on dry aggregates.
- The test should be repeated at least two times to ensure accuracy.
- The test results should be reported as the average of the two trials.
Discussion and Conclusion
The LA abrasion test is an important test method for evaluating the quality of coarse aggregates. A high LA abrasion value indicates that the aggregate is susceptible to wear and tear and may not be suitable for use in applications such as road construction. Conversely, a low LA abrasion value indicates that the aggregate is more resistant to wear and tear and may be suitable for use in these applications.
References
ASTM C131/C131M-20. (2020). Standard Test Method for Resistance to Degradation of Small-Size