Introduction
Spawn is the eggs and sperm released or deposited into water by aquatic animals (fishes). To spawn refers to a process of releasing the eggs and sperm, the act of both sexes is called Spawning. Spawning is the process of artificial or natural fertilization or reproduction process of fishes.
The process of spawning involves females releasing oval (unfertilized eggs) into the water often in large while male simultaneously releases spermatozoa (milt) to fertilize the eggs.
Objective(s) of the Experiment
The main objective of spawning is the artificial fertilization and reproduction process of fishes (Catfishes) where the female releases an unfertilized eggs into the water then a male releases milt into it which fertilizes the eggs and produce millions of catfish.
Selection of Specimen and Equipments Needed
- Brood stock selection: A male and female of the African catfish can be easily recognized. The male has a distinct sexual papilla, elongated and located just behind the anus. It is usually red at the tip for sexually ready males. A genital press on the belly of a gravid females (belly is heavy and carrying good quantities of eggs) towards the genital opening releases the ripe eggs (big in size, ability to see the nucleus in the eggs, and is grey or brown in colour) indicating the readiness and viability of the female. The reproductive organs of a ready female has a swollen, usually reddish genital opening.
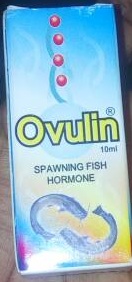
- Ovulin or Ovaprin injection: It is injected to the gravid female using hypodermic syringe, which helps to make the fish ready to release the eggs without stress.
3. Hypodermic syringe
4. Blade
5. Bowls
6. A big tank

7. Spawning net
8. Hoses
9. Stones
10. Spoon, towels.
Procedures
- Identity and separate the sexes
- Select and check for a gravid female
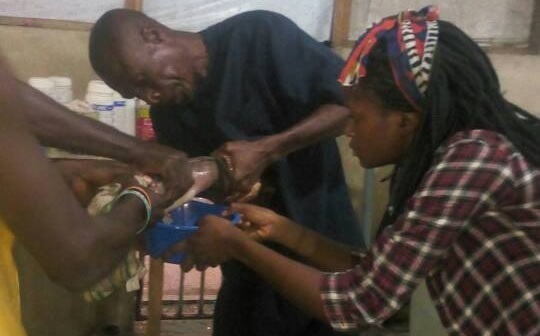
- Weigh the fish, and prepare the female catfish for injection (0.5ml/1kg). Therefore if the female weigh 2kg, the ovulin injection to be given to it is 1mL. Administer the injection below the lateral line gently and leave the fish in a clean water for 8-10 hours.
- Bring the fish out after 8-10hours gently and cover the head with a clean, moist towel. Wipe the body of the fish dry using a dry soft towel, then begin to strip off the eggs gently into a clean and dry bowl.

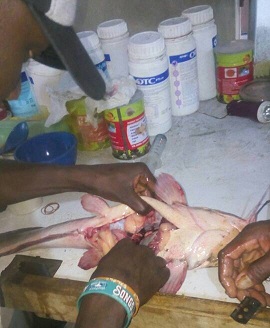
5. Bring the male out, kill it, turn the belly up and cut it to bring out the 2 milt sac. Remove the milt sac cut the testicle into bits to release the sperm.
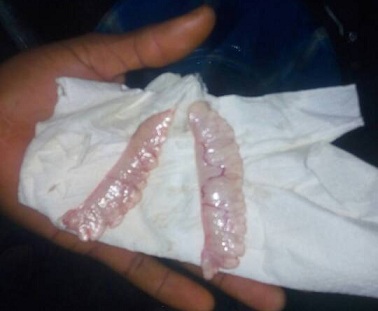
6. Cut the milt into the stripped eggs in the bowl then mix thoroughly and add fresh clean water which makes the milt active and motile, it initiate the external fertilization process and last for only about 60seconds. (Stir the mixture gently with a spoon during the 60 sec to prevent eggs from sticking together).
7. Then spread the eggs inside the incubators (tanks) on the spawning net which is completely immersed in water and however sits on two hoses and four stones which keeps it suspended in the water.
8. You wait for 24 hours to remove the spawning net, hoses and stones.

Results and Calculations
- A catfish that weigh 500g has the weight of the egg to be 50g.
- 1g = 700eggs. Thus, 50g = 35,000eggs
- Therefore, for example, if a catfish weigh 700g, the weight of the eggs will be 70g, while the number of eggs to be produced will be 49,000 eggs.
This calculation helps to know the total number of fry to be expected after spawning, and helps to prepare all the necessary things required to raise them to fingerlings or table size.
Conclusion
One of the most important limiting factors in fish production is the Water Quality, It refers to anything in the water, be it physical, chemical, or biological that affect the production of fish.
The key water quality parameters for fish production and need to be check are: Temperature, Oxygen, pH, Alkalinity, Hardness and Nitrogenous Wastes. The recommended ranges for these properties are shown in the table below:

The objective of water quality is to provide a stress free environment that meet the physical, chemical, and biological standard for the fish normal health and production performance.
Spawning of Fish (0 downloads )