There are different types of stains, namely gram stain, capsule stain, endospore stain and acid fast stain. Only acid fast stain is described in this procedure. Click on the other types of staining below to learn about them.
Introduction
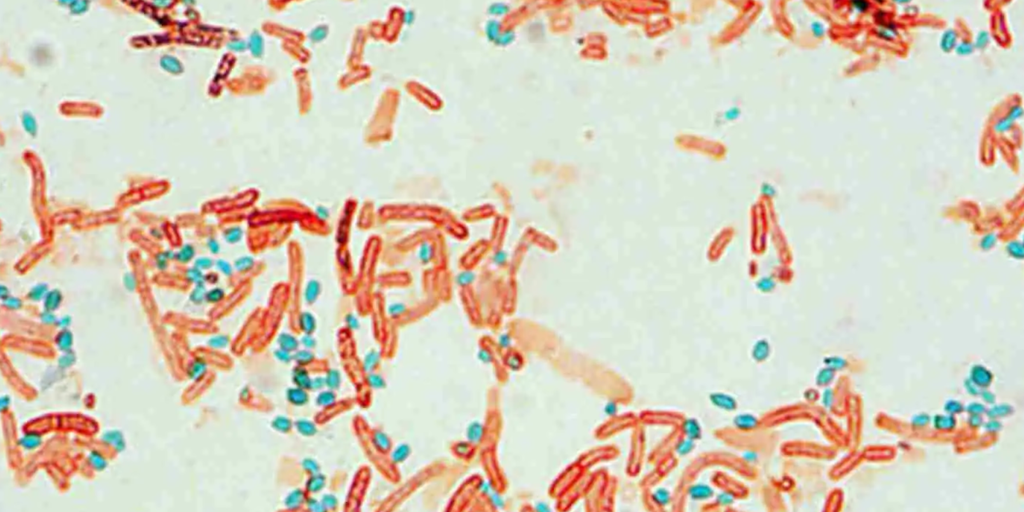
Endospore Stain is a differential stain which stains bacterial endospores or spores. Endospores may be located in the middle of the cell (central), at the end of the cell (terminal) or very close to the end (sub terminal).
Malachite green is the primary stain in endospore staining procedure, which stains both vegetative cells and endospores. Heat is required to penetrate the endospore coat. Once the cells have cooled, the cells are decolorized with water, which selectively removes the primary stain from the vegetative cells. Safranin is then applied which stains the decolorized vegetative cells pink. At the end of the procedure, the endospores are dark green.
Reagents Needed
- Malachite green
- Safranin
Procedures
- Prepare a bacterial smear on a clean glass slide, air dry and heat fix the slide.
- Place the slide on top of the beaker of water placed on an electric hot plate and let steam for 5 minutes
- Saturate the smear with malachite green and allow to sit for 2-3 minutes. Continuously add the malachite green to avoid drying.
- Allow the slide to cool
- Tilt the slide and rinse with distilled water
- Cover the slide with safranin and allow to sit for 30 seconds.
- Tilt the slide and rinse with distilled water.
- Blot the slide dry with absorbent paper.
- Observe the slide under oil immersion.
References
- Keiser, G.E. ‘Laboratory manual’
- Cain, D., Hanks, H., Weis, M., Bottoms, C., and Lawson J. ‘Microbiology Laboratory Manual Biol 2421L Revised Spring Edition’